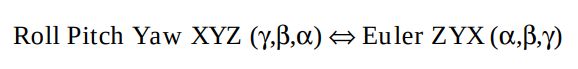
- Euler angles refer to the angles in a sequence of rotations in a body-fixed frame.
- Roll-Pitch-Yaw angles as a sequence of rotations relative to the space frame.

Example
- Rotation Matrix of camera frame respect to imu/body frame
- Intrinsic: [ x: -90, y: 90, z: 0 ] === EulerXYZ about the body frame
- Extrinsic: [ x: -90, y: 0, z: -90 ] === EulerZYX about the fixed frame
- Both start from axis-X first, then axis-Y then axis-Z
Code
Eigen::AngleAxisd rotation_x = Eigen::AngleAxisd(-0.5 * M_PI, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX());
Eigen::AngleAxisd rotation_y = Eigen::AngleAxisd(0.5 * M_PI, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY());
Eigen::AngleAxisd rotation_z = Eigen::AngleAxisd(-0.5 * M_PI, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ());
cout << "[FIXED/EULER] Rotation: " << endl
<< std::setprecision(2) << rotation_z.matrix() * rotation_x.matrix() << endl;
cout << "[roll-pitch-yaw] Rotation: " << endl
<< std::setprecision(2) << rotation_x.matrix() * rotation_y.matrix() << endl;https://web.mit.edu/2.05/www/Handout/HO2.PDF https://math.stackexchange.com/a/1681118/1133515